Android开发高手课 【第四节】 课后作业解析 —— 内存监控,分析dump下来的内存快照
这一节的目的是监控内存的变化,课后主要是做了一个使用haha库检查dump下来的heap文件,如果包含两张一模一样的bitmap文件,则输出。
Demo内容
首先,需要将内存的Heap先dump下来,为了方便起见,这里直接显示的声明了一个文件。
1 | override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { |
将内存快照dump下来之后,就可以使用我们打出的jar包去分析这个hprof文件了。以下就是如何使用HaHa库分析的代码:
1 | public class Main { |
HaHaHelper:
1 | public class HaHaHelper { |
DetectorResult:
1 | //结果类 |
上面就是分析heap的三个关键类,完成后,我们直接将手机中的hprof文件pull到本地,然后运行jar包,就可以得到如下的输出:
1 | duplcateCount: 2 |
关于打jar包时遇到的一些问题
在做课后demo的时候,遇到了一个问题就是在使用gradle 的 java plugin 的时候,当打包成jar包之后,发现没有将第三方的依赖打入jar包。检查后发现是声明依赖与configurations获取依赖不一致导致的,以下是修改之前的gradle文件:
1 | apply plugin: 'java' |
可以看到,dependancies声明的时候,我使用的是 implementation 而在下面的 task 中,在遍历依赖树的时候,使用的是 configurations.compile ,这时得到的 compile.size() 为0。很明显是因为依赖没有获取到。Java 的classpath 分为 compile-classpath 以及 runtime-classpath。所以需要首先了解到 implementation 是对应的哪一种运行环境,可以从gradle的官方文档中了解相关的信息:Java_libiary_configurations_graph
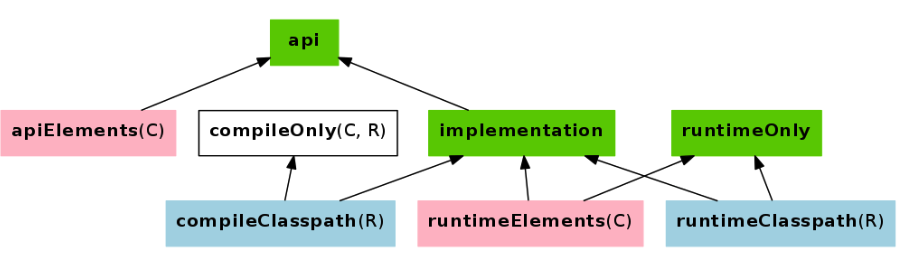
上图是官网中的一张图,可以看到 implementation 应该使用 compileClasspath 或者 runtimeClasspath ,而官方也建议使用 implementation代替 compile ,下面是gradle blog对于应该使用哪些声明的一些建议:
More uses cases, more configurations
You might be aware of the
compileOnlyconfiguration that was introduced in Gradle 2.12, which can be used to declare dependencies which are only required when compiling a component, but not at runtime (a typical use case is libraries which are embedded into a fat jar or shadowed). Thejava-libraryplugin provides a smooth migration path from thejavaplugin: if you are building an application, you can continue to use thejavaplugin. Otherwise, if it’s a library, just use thejava-libraryplugin. But in both cases:
- instead of the
compileconfiguration, you should useimplementationinstead- instead of the
runtimeconfiguration, you should useruntimeOnlyconfiguration to declare dependencies which should only be visible at runtime- to resolve the runtime of a component, use
runtimeClasspathinstead ofruntime.
根据上面的一些分析,只需要把 上面的 build.gradle 中的 configurations.compile 修改为 configuration.compileClasspath 就可以了。此时,打出的jar包中也会包含有三方依赖。